Types of window

|

|

|
Windows are openings fitted with glass to admit light and allow people to see out. They are often openable to allow ventilation. Although the historic use of glass dates back to the Romans, glass windows only became common domestically in England in the early-17th century, gradually becoming more versatile and widespread as plate glass processes were perfected during the Industrial Age.
For more information see: Window.
There are a number of ways of classifying window types:
Contents |
[edit] Frame material
[edit] Type of glass
- Acrylic.
- Annealed glass.
- Fire-resistant glass.
- Float glass.
- Fully tempered glass.
- Glass brick.
- Heat soaked tempered glass.
- Heat strengthened glass.
- Insulated glazing units.
- Laminated glass.
- Low-emissivity glass (Low-E glass).
- Polycarbonate.
- Self-cleaning glass.
- Stained glass.
- Toughened glass.
- Wired glass.
For more information see: Glass.
[edit] Type of glazing
For more information see: Windows.
[edit] Cavity fill
- Vacuum.
- Argon.
- Krypton.
- Xenon.
For more information see: Windows.
[edit] Overall design
- Bay: Multi-panel windows that project in front of the external wall line, supported by a sill height wall.
- Bow: A curved bay window.
- Bullseye: A circular window.
- Clerestory: Bands of windows across the tops of buildings that allow natural light in without compromising privacy or security.
- Curtain wall: A non-structural cladding systems generally associated with large, multi-storey buildings.
- Display window: Intended for the display of products or services on sale within a building.
- Dormer: A small roofed structure that projects outwards from the main pitched roof of a building.
- Glass mullion system: Sheets of tempered glass held in position by clamps and joined by a structural silicone sealant or by metal patch plates
- Multi-lite: Windows glazed with small panes of glass separated by glazing bars, or muntins.
- Patent glazing: A non-load bearing, two-edge support cladding system.
- Picture window: A large fixed window that lets in the maximum amount of light and provides external views.
- Roof window: A window that is in the same plane as the surrounding roof, and has a minimum pitch of 15 degrees.
- Rooflight / skylight: A dome light, lantern light, skylight, ridge light of glazed barrel vault installed on an upstand, so it is not in the same plane as the surrounding roof.
- Sidelight: Positioned beside a door or main window.
- Toplight: These are usually above doors.
- Transom window: A horizontal window that is commonly mounted above a door or another window to let in more light.
- Storm glazing. Temporary external glazing system.
- Fanlight. Glazed area above a door.
- Vision panel: Transparent or translucent sections built into doors or partitions.
For more information see: Windows.
[edit] Method of opening
- Awning: Hinged at the top and opened outwards.
- Bi-fold: Made up of a number of individual sashes, usually 2, 3 or 4, hinged together.
- Casement: An opening window fixed to the frame by hinges along one of its edges.
- Fixed light: A window that is fixed in place and cannot be opened.
- Louvre: A series of parallel pieces of glazing that are hung on central pivots.
- Pivot: Hung on one hinge at centre points on each of two opposite sides allowing the window to revolve when opened.
- Sidehung: A variation on a casement window, side opening controlled by tracks and slides.
- Tilt and slide: Tilts inwards at the top and slides horizontally behind the fixed pane.
- Tilt and turn: Include a mechanism that allows them to tilt inwards from one edge or to open inwards from one side.
- Topguided: Tracks and slides enable the top to slide downwards whist the bottom opens out.
- Vertical slider / sash: Glass is fitted in ‘sashes’ (moveable panels) that slide vertically past each other.
For more information, see Domestic windows.
[edit] Window Energy Rating
The Window Energy Ratings (WER) is a scale developed by the British Fenestration Ratings Council (BFRC) to measure the thermal performance of windows. The BFRC label indicates the rating of the window on a scale running from A+ (the most energy efficient) to G (the least efficient).
For more information, see Window Energy Rating
[edit] Style
See: Architectural styles.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki.
- Angular selective shading systems.
- Architectural styles.
- Bespoke window.
- Bay window.
- Birds and building collisions.
- Bullseye window.
- Clerestory.
- Crittall metal windows.
- Domestic windows.
- Double glazing.
- Double glazing v triple glazing.
- Easily accessible window.
- Fenestration.
- Furnishings.
- Glass manifestation.
- Glass.
- Glazing.
- Historic steel-framed windows.
- Jamb.
- Laced window.
- Light well.
- Louvre (or louver).
- Plate glass.
- Sash windows.
- Security glazing.
- Stained glass.
- Triple glazing.
- Types of blinds.
- Types of door.
- Vision panel.
- Window and door schedules.
- Window Energy Rating.
- Window frame.
- Window parts.
- Windows.
- Yorkshire Lights.
Featured articles and news
What they are, how they work and why they are popular in many countries.
Plastic, recycling and its symbol
Student competition winning, M.C.Esher inspired Möbius strip design symbolising continuity within a finite entity.
Do you take the lead in a circular construction economy?
Help us develop and expand this wiki as a resource for academia and industry alike.
Warm Homes Plan Workforce Taskforce
Risks of undermining UK’s energy transition due to lack of electrotechnical industry representation, says ECA.
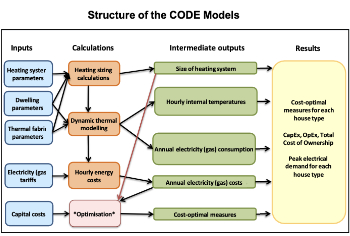
Cost Optimal Domestic Electrification CODE
Modelling retrofits only on costs that directly impact the consumer: upfront cost of equipment, energy costs and maintenance costs.
The Warm Homes Plan details released
What's new and what is not, with industry reactions.
Could AI and VR cause an increase the value of heritage?
The Orange book: 2026 Amendment 4 to BS 7671:2018
ECA welcomes IET and BSI content sign off.
How neural technologies could transform the design future
Enhancing legacy parametric engines, offering novel ways to explore solutions and generate geometry.
Key AI related terms to be aware of
With explanations from the UK government and other bodies.
From QS to further education teacher
Applying real world skills with the next generation.
A guide on how children can use LEGO to mirror real engineering processes.
Data infrastructure for next-generation materials science
Research Data Express to automate data processing and create AI-ready datasets for materials research.
Wired for the Future with ECA; powering skills and progress
ECA South Wales Business Day 2025, a day to remember.
AI for the conservation professional
A level of sophistication previously reserved for science fiction.
Biomass harvested in cycles of less than ten years.
An interview with the new CIAT President
Usman Yaqub BSc (Hons) PCIAT MFPWS.
Cost benefit model report of building safety regime in Wales
Proposed policy option costs for design and construction stage of the new building safety regime in Wales.
Do you receive our free biweekly newsletter?
If not you can sign up to receive it in your mailbox here.























Comments
Really helpful breakdown of the different window styles, it’s easy to forget how much variety there is beyond the basics like casement or sash. I’ve noticed that a professional window cleaning company in San Diego often highlights how cleaning methods differ depending on whether you’re dealing with bay, tilt-and-turn, or even louvre windows.